Hi All
I spent some time digging into ease of manufacture of DNA stains that are suitable for qPCR. For those looking for standard gel stains, we recommend thiazole orange which is sold in powder form and works out at <$5 per 1ml in terms of material costs:
Many of the SYTO dyes are now off patent but they look a bit complicated (to my eyes but talk to a synthetic chemist and they will probably be able to help you figure out the protocol).
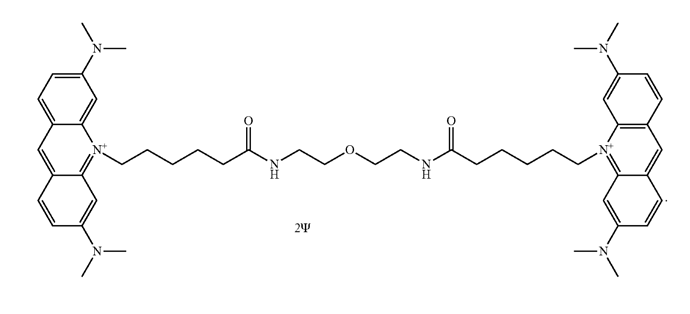
EvaGreen® dye is very simple, it is two acridine orange molecules with a bridge. The dye and and its applications are covered under patent US patent nos. 7,803,943 and 7,776,567 and family, the latest of which is US 7803943 B2.
I’m posting this information here because expiry is coming up and then it will fall in the public domain. It can already be manufactured and sold in jurisdictions where it is not protected by patent, and used under any relevant research exemptions that exist in areas where it is patented.
In Europe (EP 1863933 B1), China (CN 102942566 B), South Korea (KR 101333434 B1) and Japan (JP 5249013 B2) the patent will expire on 17 March 2026, in the US there is a term extension and the Anticipated Termination Date is 10 Jan 2027. These are all of the jurisdictions listed on USPTO Global Dossier but you should check locally for coverage.
The structure is published here:
Shoute, Lian CT, and Glen R. Loppnow. “Characterization of the binding interactions between EvaGreen dye and dsDNA.” Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 20.7 (2018): 4772-4780. DOI: 10.1039/C7CP06058K
(Image from US Patent US 7803943 B2)
Below is the protocol for synthesising Eva Green, about $500 of reagents will yield approx $500k worth of dye (based on our calculations from a single batch - your mileage and input costs may vary!).
We’ll update with more info, QA/QC data and costings…
Huge thanks to Dr Ishtiaq Ahmed at University of Cambridge for his help with this!
Jenny
Synthesis of AOAO-12/EvaGreen in US Patent US 7803943 B2
Materials
- Ethyl 6-bromohexanoate | CAS No. 25542-62-5
- Acridine Orange base | CAS No. 494-38-2
- Chlorobenzene | CAS No. 108-90-7
- TSTU | CAS No. 105832-38-0
- 2,2′-Oxydiethylamine dihydrochloride | CAS No. 60792-79-2
Preparation of 10-(5-Carboxypentyl)acridine orange, chloride salt (1)
One equivalent of ethyl 6-bromohexanoic acid was added to a suspension of 5 g of acridine orange (Aldrich) in 10 mL of chlorobenzene. The resulting mixture was stirred at 90-100° C overnight. The hot reaction mixture was poured into ~200 mL of EtOAc. The orange precipitate was collected by filtration and dried under vacuum.
Preparation of AOAO-12/EvaGreen (Dye No. 19 of Table 1) in US Patent US 7803943 B2
The crude product (5 g) was suspended in ~100 mL methanol and 3 equivalents of NaOH dissolved in 30 mL H2O. The suspension was stirred at room temperature for 24 h. Methanol was removed by evaporation, and the remaining aqueous solution was acidified with concentrated HCl. About 50 mL saturated NaCl was added to precipitate the product. The product was collected by filtration and then dried under vacuum at 45° C for 24 hours.
Et3N (0.15 mL, 1.05 mmol) and TSTU (320 mg, 1.05 mmol) were added to a suspension of (1) 10-(5-carboxypentyl)acridine orange chloride salt (147 mg, 0.35 mmol) in DMF (5 mL) at room temperature. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 15 minutes, followed by the addition of Et3N (0.1 mL) and 2,2′oxybis(ethyl-amine)dihydrochloride (25 mg, 0.14 mmol). After the mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight, EtOAc (20 mL) was added to precipitate the product. The crude product was re-dissolved in DMF and precipitated out again with EtOAc. The solid (250 mg) was separated by centrifugation.